Wednesday, August 29, 2007
Saffron
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:43 AM
![]()
![]()
Honey:Medicinal uses and health
A study found that certain anti-oxidants and vitamins are found in honey in concentrations similar to those in some fruits and vegetables.
Hydrogen peroxide in honey is activated by dilution. However, unlike medical hydrogen peroxide, commonly 3% by volume, it is present in a concentration of only 1 mmol/l in honey. Iron in honey oxidizes the oxygen free radicals released by the hydrogen peroxide.
glucose + H2O + O2 → gluconic acid + H2O2
When used topically (as, for example, a wound dressing), hydrogen peroxide is produced by dilution with body fluids. As a result, hydrogen peroxide is released slowly and acts as an antiseptic.
Topical honey has been used successfully in a comprehensive treatment of diabetic ulcers when the patient cannot use other topical antibiotics.
The pH of honey is commonly between 3.2 and 4.5. This relatively acidic pH level prevents the growth of many bacteria.
According to recent findings, honey may have some significant nutraceutical effects (or positive long-term health effects resulting from honey's consumption). In addition to its primary carbohydrate content, honey often contains polyphenols, which can act as antioxidants. Antioxidants in honey have even been implicated in reducing the damage done to the colon in colitis.Furthermore, some studies suggest that honey may be effective in increasing the populations of probiotic bacteria in the gut, which may help strengthen the immune system, improve digestion, lower cholesterol and prevent colon cancer.
Some studies suggest that the topical use of honey may reduce odors, swelling, and scarring when used to treat wounds; it may also prevent the dressing from sticking to the healing wound. Honey has been shown to be an effective treatment for conjunctivitis in rats. Honey (especially when combined with lemon) is often taken orally by pharyngitis and laryngitis sufferers, in order to soothe them. Though widely believed to alleviate allergies, local honey has been shown to be no more effective than placebos in controlled studies. This may be due to the fact that most seasonal allergies are caused by tree and grass pollens, which honeybees do not collect.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:39 AM
![]()
![]()
Honey and Islamic tradition
The Qur'an mentions rivers of honey in paradise.
"And thy Lord taught the bee to build its cells in hills, on trees and in (men's) habitations...there issues from within their bodies a drink of varying colours, wherein is healing for mankind. Verily in this is a Sign for those who give thought".
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:35 AM
![]()
![]()
Tuesday, August 28, 2007
Medicinal mushrooms
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
2:27 PM
![]()
![]()
Apple: Medicinal value
A group of chemicals in apples could protect the brain from the type of damage that triggers such neurodegenerative diseases as Alzheimer's and Parkinsonism. Chang Y. 'Cy' Lee of the Cornell University found that the apple phenolics, which are naturally occurring antioxidants found in fresh apples, can protect nerve cells from neurotoxicity induced by oxidative stress. The researchers used red delicious apples from New York State to provide the extracts to study the effects of phytochemicals. Lee said that all apples are high in the critical phytonutrients and that the amount of phenolic compounds in the apple flesh and in the skin vary from year to year, season to season and from growing region to growing region (November/December 2004 issue of the Journal of Food Science). The predominant phenolic phytochemicals in apples are quercetin, epicatechin, and procyanidin B2
The seeds are mildly poisonous, containing a small amount of amygdalin, a cyanogenic glycoside, but a large amount would need to be chewed to have any toxic effect.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
2:13 PM
![]()
![]()
Coconut Palm
The white, fleshy part of the seed is edible and used fresh or dried in cooking.
The cavity is filled with coconut water which contains sugar, fibre, proteins, antioxidants, vitamins and minerals. Coconut water provides an isotonic electrolyte balance, and is a highly nutritious food source. It is used as a refreshing drink throughout the humid tropics. It can also be used to make the gelatinous dessert nata de coco. Mature fruits have significantly less liquid than young immature coconuts; barring spoilage, coconut water is sterile until opened.
Sport fruits are also harvested, primarily in the Philippines, where they are known as macapuno.
Coconut milk is made by processing grated coconut with hot water or milk, which extracts the oil and aromatic compounds. It should not be confused with the coconut water discussed above, and has a fat content of approximately 17%. When refrigerated and left to set, coconut cream will rise to the top and separate out the milk.
The leftover fibre from coconut milk production is used as livestock feed.
The sap derived from incising the flower clusters of the coconut is fermented to produce palm wine, also known as "toddy" or, in the Philippines, tuba. The sap can also be reduced by boiling to create a sweet syrup or candy.
Apical buds of adult plants are edible and are known as "palm-cabbage" (though harvest of these kills the palm).
Ruku Raa is an extract from the young bud, a very rare type of nectar collected and used as morning break drink in the islands of Maldives reputed for its energetic power keeping the "raamen"(nectar collector) healthy and fit even over 80 and 90 years old. And by-products are sweet honey-like syrup and creamy sugar for desserts.
The interior of the growing tip may be harvested as heart-of-palm and is considered a rare delicacy. Harvesting this also kills the tree. Hearts of palm are often eaten in salads, sometimes called "millionaire's salad".
Newly germinated coconuts contain an edible fluff of marshmallow-like consistency called coconut sprout, produced as the endosperm nourishes the developing embryo.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
2:08 PM
![]()
![]()
Coriander, its medical uses
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:54 PM
![]()
![]()
Toxic compounds in potato
Breeders try to keep solanine levels below 200 mg/kg (200 ppmw). However, when these commercial varieties turn green, even they can approach concentrations of solanine of 1000 mg/kg (1000 ppmw). In normal potatoes though, analysis has shown solanine levels may be as little as 3.5% of the breeders' maximum, with 7–187 mg/kg being found. The National Toxicology Program suggests that the average American consumes at most 12.5 mg/person/day of solanine from potatoes (note that the toxic dose is actually several times this, depending on body weight). Dr. Douglas L. Holt, the State Extension Specialist for Food Safety at the University of Missouri - Columbia, notes that no reported cases of potato-source solanine poisoning have occurred in the U.S. in the last 50 years and most cases involved eating green potatoes or drinking potato-leaf tea.
Solanine is also found in other plants, mainly in the mostly-deadly nightshade family, which includes a minority of edible plants including the potato and the tomato, and other typically more dangerous plants like tobacco. This poison affects the nervous system causing weakness and confusion.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:45 PM
![]()
![]()
By BBC News
The tomato plant has been engineered in a way that prevents its new genes from passing to other crops - something which has been a major concern for organic farmers and conservation groups.
New laboratory techniques also mean much higher levels of a desired health-giving protein appear in the edible tissues of the plant - the bright red fruits themselves.
The scientists envision "super tomatoes" that offer consumers substantially increased vitamin content. "We are also planning to make tomato plants that express vaccines in the fruits for oral immunisation," lead researcher Professor Ralph Bock, at the Institute of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology in Munster, told BBC News Online.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:16 PM
![]()
![]()
Tomato seedlings
German team has used only a marker gene in its experiments - to prove the approach works. More useful genes will now be incorporated into the tomatoes. The scientists write: "Given the generally very high foreign protein accumulation rates that can be achieved in transgenic chloroplasts, this system paves the way to efficient production of edible vaccines, pharmaceuticals, and antibodies in tomato."
And in an accompanying article, a US expert agreed that GM tomatoes with transformed plastids could make it easier to develop edible vaccines.
Pal Maliga, from Rutgers University in Piscataway, New Jersey, writes: "The report of plastid transformation in tomato is... a milestone achievement, and the capacity to express foreign proteins at a high level in consumable fruit should open new opportunities for engineering the next generation of medicinal products that are more palatable to the consumer."
A number of research groups are now looking to produce food crops that have enhanced nutritional or medicinal value. These new foods are sometimes referred to as nutraceuticals.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:12 PM
![]()
![]()
Regeneration of Tomatoes
Instead of introducing a gene for a particular trait into a plant's nuclear DNA, the coding sequence is put in amongst the small amount of DNA found in small cellular compartments known as plastids. In this case, the German team targeted chloroplasts, which generate energy from sunlight.
Crucially, the DNA in chloroplasts, unlike nuclear DNA, is not transmitted in pollen. So this eliminates the possibility that the modified plant's genetic material might "contaminate" other crops or pass undesirable traits to weeds.
Until now, though, chloroplast transformation has been achieved routinely only in tobacco; other plants have been sterile or shown disappointing results in the non-leafy tissues, such the fruits.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:06 PM
![]()
![]()
Tomato Sauce: the Ultimate Medicine Cabinet
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
12:56 PM
![]()
![]()
Sunday, August 26, 2007
Spinach (Spinacia oleracea)
The myth about spinach and its high iron content may have first been propagated by Dr. E. von Wolf in 1870, because a misplaced decimal point in his publication led to an iron-content figure that was ten times too high. In 1937, German chemists reinvestigated this "miracle vegetable" and corrected the mistake. Ultimately, the bioavailability of iron is dependent on its absorption. This is influenced by a number of factors. Iron enters the body in two forms: nonheme iron and heme iron. All of the iron in grains and vegetables, and about three fifths of the iron in animal food sources (meats), is nonheme iron. The much smaller remaining portion from meats is heme iron.
The larger portion of dietary iron (nonheme) is absorbed slowly in its many food sources, including spinach. This absorption may vary widely depending on the presence of binders such as fiber or enhancers, such as vitamin C. Therefore, the body's absorption of non-heme iron can be improved by consuming foods that are rich in vitamin C. However, spinach contains high levels of oxalate. Oxalates bind to iron to form ferrous oxalate and remove iron from the body. Therefore, a diet high in oxalate (or phosphate or phytate) leads to a decrease in iron absorption.
Spinach also has a high calcium content. However, the oxalate content in spinach binds with calcium decreasing its absorption. By way of comparison, the body can absorb about half of the calcium present in broccoli, yet only around 5% of the calcium in spinach. Oxalate is one of a number of factors that can contribute to gout and kidney stones. Equally or more notable factors contributing to calcium stones are: genetic tendency, high intake of animal protein, excess calcium intake, excess vitamin D, prolonged immobility, hyperparathyroidism, renal tubular acidosis, and excess dietary fiber.
Spinach still has a large nutritional value, especially when fresh, steamed, or quickly boiled. It is a rich source of vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin K, magnesium, and several vital antioxidants. Recently, opioid peptides called rubiscolins have also been found in spinach. It is a source of folic acid, and this vitamin was first purified from spinach. To benefit from the folate in spinach, it is better to steam it than to boil it. Boiling spinach for four minutes can halve the level of folate.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:59 AM
![]()
![]()
Saturday, August 25, 2007
Medicinal,Cosmetic & Pragmatic value of Mentha
In Rome, Pliny recommended that a wreath of mint was a good thing for students to wear since it was thought to 'exhilarate their minds'. Some modern research suggests that he was right.Mint leaves are often used by many campers to repel mosquitoes. It is also said that extracts from mint leaves have a particular mosquito killing capability.Mint oil is also being used as an environmentally friendly insecticide for its ability to kill some common pests like wasps, hornets, ants and cockroaches.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
4:33 AM
![]()
![]()
Thursday, August 23, 2007
Medicinal and nutritional properties of Mango
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
5:02 AM
![]()
![]()
Tulasi as an Ayurvedic medicine
Tulasi’s extracts are used in ayurvedic remedies for common colds, headaches, stomach disorders, inflammation, heart disease, various forms of poisoning, and malaria. Traditionally, tulasi is taken in many forms: as an herbal tea, dried powder, fresh leaf, or mixed with ghee. Essential oil extracted from Karpoora Tulsi is mostly used for medicinal purposes and in herbal toiletry. For centuries, the dried leaves of Tulasi have been mixed with stored grains to repel insects.
Recent studies suggest that Tulasi may be a COX-2 inhibitor, like many modern painkillers, due to its significant amount of Eugenol (1-hydroxy-2-methoxy-4-allylbenzene). Studies have also shown Tulsi to be effective for diabetes, by reducing blood glucose levels. The same study showed significant reduction in total cholesterol levels with Tulsi. Another study showed that Tulsi's beneficial effect on blood glucose levels is due to its antioxidant properties.
Tulasi also shows some promise for protection from radiation poisoning and cataracts. Some Vaishnavites do not use Tulasi for medicine, though, out of reverence. However, the use of Tulsi for purification and as a medicine is widespread throughout India.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
4:55 AM
![]()
![]()
Garlic as Anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, anti-fungal, and anti-bacterial usage
Garlic, like onion, contains compounds that inhibit lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase, (the enzymes that generate inflammatory prostaglandins and thromboxanes), thus markedly reducing inflammation. These anti-inflammatory compounds along with the vitamin C in garlic, especially fresh garlic, make it useful for helping to protect against severe attacks in some cases of asthma and may also help reduce the pain and inflammation of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition, allicin, one of the sulfur-compounds responsible for garlic's characteristic odor, is a powerful anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and anti-viral agent that joins forces with vitamin C to help kill harmful microbes. In research studies, allicin has been shown to be effective not only against common infections like colds, flu, stomach viruses, and Candida yeast, but also against powerful pathogenic microbes including tuberculosis and botulism.
Although garlic alone appears unable to prevent infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), the bacterium responsible for most peptic ulcers, as well as gastritis, frequently eating this richly flavored bulb may keep H. pylori from doing much damage. A study recently conducted at Faith University in Istanbul, Turkey, compared two groups of healthy individuals: one was selected from individuals who regularly ate lots of raw and/or cooked garlic, while the other group was composed of individuals who avoided it. For 19 months, blood samples were regularly collected from both groups and evaluated for the presence of H.pylori. While the incidence of H.pylori was pretty comparable-the bacterium was found in 79% of garlic eaters and 81% of those who avoided garlic-the garlic-consuming group had a clear advantage in that antibodies to H.pylori were much lower in their blood compared to those who ate no garlic. (Antibodies are formed when the immune system reacts to anything it considers a potential pathogen, so less antibodies to H.pylori means less of the bacterium was present.) Among those who ate garlic, those who ate both raw and cooked garlic had even lower levels of antibodies than those who ate their garlic only raw or only cooked. Laboratory studies recently conducted at the University of Munich, Germany, help explain why garlic may be such a potent remedy against the common cold. In these studies, garlic was found to significantly reduce the activity of a chemical mediator of inflammation called nuclear transcription factor (NF) kappa-B.
NF kappa-B is itself activated as part of the immune system's inflammatory response to invading organisms and damaged tissue. So, anything that sets off an inflammatory response (e.g. allergenic foods, a cold or other infection, physical trauma, excessive exercise, excessive consumption of foods containing high levels of omega-6 fatty acids-such as meat, corn or safflower oil) can trigger a surge in NF kappa-B, which in turn not only promotes inflammation but sets up ideal conditions for viruses, including HIV, to replicate. In the blood samples tested in these German studies, unfertilized garlic caused a 25% drop in NF kappa-B activity, while sulfur-fertilized garlic lowered NF kappa-B activity by a very robust 41%.
Results of two studies suggest that garlic is a potent antibiotic, even against strains that have become resistant to many drugs. One study conducted at the University of California Irvine Medical Center and published in the December 2003 issue of Nutrition showed that garlic juice, even when diluted up to 1:128 of the original juice, demonstrates significant antibacterial activity against a spectrum of pathogens including antibiotic-resistant strains such as methicillin- and ciprofloxacin-resistant staphylococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, and ciprofloxacin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. A second study found that garlic was able to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MSRA) from human patients that was injected into laboratory animals.(MSRA is one of the antibiotic resistant bacteria whose incidence has risen dramatically in recent years in hospitals)
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
4:43 AM
![]()
![]()
Garlic as Anti-carcinogenic usage
A cancer-causing heterocyclic amine, PhIP is thought to be one reason for the increased incidence of breast cancer among women who eat large quantities of meat because it is rapidly transformed into DNA-damaging compounds.Diallyl disulphide (DAS), an organosulfur compound that gives garlic its unique flavor, has been shown to inhibit the transformation of PhIP into carcinogens. DAS blocks this transformation by decreasing the production of the liver enzymes (the Phase I enzymes CYP1A1, CYP1A2 and CYP1B1) that transform PhIP into activated DNA-damaging compounds.
In addition, DAS signals the genes responsible for producing two protective antioxidant enzymes, (glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), which help protect the body against harmful compounds such as those produced from PhIP. These findings suggest that making garlic, onion, chives and other Allium vegetables, all of which contain DAS, a staple part of your healthiest way of eating may help in preventing breast cancer induced by PhIP in well-done meats. And enjoying these DAS-rich foods may help protect the men you love as well. Consumption of Allium vegetables has also been associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
4:38 AM
![]()
![]()
Medicinal use of Aloe vera
A. vera's beneficial properties may be attributed to mucopolysaccharides present in the inner gel of the leaf, especially acemannan (acetylated mannans). An injectable form of acemannan manufactured and marketed by Carrington Laboratories as Acemannan Immunostimulant™ has been approved in the USA for treatment of fibrosarcoma (a type of cancer) in dogs and cats after clinical trials. It has not been approved for use by humans, and although it is not a drug its sale is controlled and it can only be obtained through a veterinary doctor.
Cosmetic companies add sap or other derivatives from A. vera to products such as makeup, moisturisers, soaps, sunscreens, shampoos and lotions, though the effectiveness of Aloe vera in these products remain unknown. A. vera gel is also alleged to be useful for dry skin conditions, especially eczema around the eyes and sensitive facial skin.
An article published in the British Journal of General Practice suggests that A. vera is effective at treating athlete's foot.The topical application of A. vera is not an effective preventative for radiation-induced injuries.
Whether or not it promotes wound healing is unknown, and even though there are some promising results, clinical effectiveness of oral or topical A. vera remains unclear at present.
Aloe vera juice may help some people with ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
4:09 AM
![]()
![]()
Herbs
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:52 AM
![]()
![]()
Antioxidants and Immune System
Role of Vitamin C in Immune System:
According to Contagious Disease Control (CDC) spokesperson, most patients do not live more than three years after diagnosis. Vitamin C apparently stabilizes the loss of T- helper cells.
What are T -helper cells? In order to understand what they are, an explanation of T - cell is necessary .The T -cells along with B-cells are macrophages, white blood cells (leukocytes) that help protect the body against invading bacteria and viruses. Both d1e B-cells and the T- cells originate in the liver and then migrate to the bone marrow, where they follow different lines of development, specializing into various kinds of "stems," or precursor cells. The T cells then move from the bone marrow to the thymus gland. Hence, T -cells get their name from 'thymus," while B-cells are named from bone marrow.
The B-cells are responsible for producing antibodies, which are substances specifically matched to each individual antigen (allergen). The job of the antibodies is to help in neutralizing or destroying antigens. When an antigen, undergoes a physical change. For example, the B-cell increases in size and divides into several cells known as plasma cells which secrete the antibodies. Some of these antibodies then circulate throughout body, where they can interact with the corresponding antigen. 'Others are secreted on the surface of B-cells and help in recognizing antigens.
It is because they release antibodies into the body fluids to combat antigens that the B-cells are said to be involved in humoral (blood and lymph) immunity. Meanwhile, the T -cells develop into various specialized kinds of cells responsible for cell medicated immune reactions. Instead of reacting to the presence of antigens by producing antibodies, the T -cells influence neighboring white blood cells and other cells. T - cells are there to fight bacteria, fungi, parasites, and intracellular viruses (the ones that attack from within the body's cells).
Some T -cells influence other cells by turning on or off reactions in the immune system. T -helper cells may induce B-cells to respond to the presence of an antigen, and they may also stimulate activity in other T -cells. T -suppressor cells operate in the opposite direction, regulating the immune response by turning off certain cell and attach to cells and spread once they have infected them. With my program there is no need for AZT.
Vitamin C as a free radical scavenger:
Vitamin C is very effective in killing free radicals. When you take Vitamin C in massive doses, it reacts as a free radical scavenger. Free radicals are free roaming molecules that, if unchecked, can damage cells, produce genetic changes, and is one of the main causes of kaposi sarcoma cancer in AIDS patients. Vitamin C will disarm these free radicals, and at the same time step up the immune system.
Role of Aloe Vera in AIDS
After many months of observation and reading a report by Ron Mealy on Aloe Vera concentrate, I decided to include Aloe Vera juice concentrate in my AIDS program. We found it helps with Epstein Barr and AIDS. Everyone that took the juice concentrate stated that energy increased and they were able to sleep through the night.
A team of scientists from Texas A & M University and three other institutions say that acemannan (which is a component of Aloe Vera) purified from green, spiky AloeVera plants, appears to help drugs such as retrovir (zidovudine, a drug formerly known as AZT) and acyclovir (ACV) block the pathology associated with the human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) and herpes simplex virus (HSV). They also found that the compound interfered with HIV ability to reproduce in affected
Dr. Maurice C. Kemp, a virologist at Texas A & M’s college of Veterinary Medicine said the research suggests that one-tenth the AZT dose could be administered to AIDS patients if it is given with acemannan. Kemp’s laboratory research uses cultures of cells to study how acemannan affects the way viruses attach to cells and spread once they have infected them. With my program there is no need for AZT.
Garlic
Garlic has been used for thousands of years. An Egyptian medical papyrus dating from around 1500 BC discusses the use of garlic in 22 prescriptions. Garlic was used during World War I to fight typhus and dysentery. In World War 2, British physicians treating battle wounds with garlic reported its benefits in warding off septic poisoning and gangrene. In 1944, a Chester J. Cavallito, identified garlic's strong odour as the compound, Allicin, as an antibiotic.
Tests found raw garlic more powerful than penicillin and tetracycline. Literally hundreds of studies confirm garlic as a broad-spectrum antibiotic against a long list of microbes that spread disease, including botulism, tuberculosis, diarrhea, staphylococcus, dysentery and typhoid. Garlic is antibacterial, antifungal, an- tiparasitic, antiprotozoan, and antiviral.
The National Library of Medicine, in Bethesda, Maryland, a prestigious repository of medical literature, contains about 125 scientific papers on garlic revealing the potent compounds that appear to retard heart disease, stroke, cancer, and a wide range of infections.
Garlic can help your brain function. Dr. Garagus had noticed an article in the Chinese Medical Journal. Chinese doctors referred to the ancient practice of administering garlic. They fed and injected garlic into patients with a serious infection called cryptococcal meningitis. Of sixteen who got the garlic, eleven survived~ For a cure rate of sixty eight percent, this was not bad, considering that this infection gets in the spinal cord and into the brain. Even some powerful antibiotics can't cross the blood-brain, barrier to attack the bacteria. That meant garlic, or at least some chemical of garlic probably did travel from the blood stream or spinal fluid and into the brain, where it destroyed the bacteria, and caused no side effect unlike prescription antibiotics.
In fact, in days before man-made antibiotics, garlic was the drug of choice against TB. At the turn of the century the head of a large tuberculosis ward in Dublin reported remarkable cure rates from eating, inhaling, and smearing garlic on the chest as an ointment. Around the same time in New York City , a physician compared the effectiveness of fifty five tuberculosis treatments and found garlic the best.
The ancient Egyptians worshipped garlic. Poling the Elder, a Roman administrator and naturalist living in the first century AD recommended garlic for no fewer than sixty one ailments, and what better company could one want. Even Louis Pasteur in 1858 put a dollop of garlic in a petri dish and recorded that the bacteria died.
Researchers at George Washington University had confirmed a chemical in garlic that thinned blood. Tuberculosis is on the upswing in the United States. Major carriers of this mycobacterium are those infected with HIV. Some AIDS victims are infected by a fungal bug call M. A vlum, previously seen only in birds.
Fungal infections in the United States have doubled or tripled in the last five years. Drs. Garagusi and Delaha were seeing more blood samples infected by these strains of fungus bacteria. To see if garlic is as effective against fungi as the Chinese medical report said, Dr .Delaha peeled and ground up ten bulbs of garlic in a blender. He extracted the active ingredient, allicin, from the garlic pulp, and the result was a frozen extract of garlic. He put thirty strains of seventeen species of mycobacterium in sterile petri dishes and then introduced the garlic compound in various concentrations. Then he watched the bacteria grow in the non-garlic dishes thrive. The one with garlic in the dishes withered and died. Garlic killed or did damage to all the fungal bacteria. (AIDS patients have a big problem with fungal disease). Garlic not only did damage to fungal infection, but also to those that caused tuberculosis. In fact, it was extra potent against the TB bacteria. Better than standard antibiotics, garlic rips apart the mycobacterium cell walls or interferes with their enzymes so they starve to death. Dr. Garagus said he wished he knew, how and why garlic works.
Herbs and Plants as Healers
"Hear, hear, hear," the word of the Lord. Revelation 22 :2. "In the midst of the street of it, and on either side of the river, was there the tree of life, which bare twelve manner of fruits, and yielded her fruit every month: and the leaves of the tree were for the healing of the nations."
Psalms 104:14 "He causeth the grass to grow for the cattle, and herb for the service of man: that he may bring forth food out to the earth."
Dr. Norman Farnsworth, (the Director of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Health Sciences Center, University of Illinois at Chicago) set up computer data with about 50,000 scientific references on foods and their active chemicals. About 25 % of all prescription drugs used in the world were derived from natural plant substances. He did a study of these 140 pure drugs derived from ninety species of plants and found excellent folk remedies. In seventy-four percent of the case the purified active chemical is used to treat the same disease as the plant was reputed to cure. We owe the plant kingdom a lot.
Science first found a plant to yield a chemical benzoic acid in the sixteenth century. In 1804 the opium poppy gave us morphine. After that, plant pharmacology went into high gear. Today western medicine counts on plants to turn out such common drugs as acetyldigoxin, allantoin, aspirin, valium, bromelain, codeine, digitoxin, 1- dopa, leurocristine, papain, physostigmine, pseudoephedrine, quinine, re-serpine, scopolamine, strychnine, theophylline, xanthotoxin, camphor, and menthol capsaicin. Still only (five to ten percent) of the 250,000 plant species on the face of the earth have ever been examined.
Poke Root weed yields a drug that fights AIDS:
A drug developed from the leaves of an otherwise poisonous weed appears to be 1,000 times more potent than the drug AZT in destroying the AIDS virus, researchers said.
The University of Minnesota said the drug contains a virus fighting protein from the new leaves of pokeweed, a perennial American herb that is otherwise poisonous to humans. When used alone, the protein inhibits the production of the AIDS virus in those cells in the immune system, the researchers said. When coupled with monoclonal antibodies, inhibition of the AIDS virus production was increased as much as 1,000 fold. Clinical tests are to begin soon. Herbalist's have been using pokeroot for many years with a very good cure rate.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:42 AM
![]()
![]()
Monday, August 20, 2007
Friday, August 10, 2007
Wednesday, August 8, 2007
allicin is a valuable natural anti-oxidant to combat tuberculosis
Medical Research
DR. Najmul Islam (Reader)
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:09 AM
![]()
![]()
Tuesday, August 7, 2007
Baum’s Textbook of Pulmonary Diseases (Textbook of Pulmonary)
http://rapidshare.de/files/21758293/Baum_-_Baum_s_Textbook_of_Pulmonary_Diseases_7th_ed.pdb
(29.07 MB) or
http://www.badongo.com/file/490056
http://rapidshare.com/files/20824881/TextbkPulmonaryDisease-Baum.pdb_dl_y_ts_1173792366_z_faf83efd4084cf1ac5dadc62c49307b0_server_64.72.1
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
8:50 AM
![]()
![]()
Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine 2nd Edition
Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine 2nd_Edition. Vol. 4 S-Z Pdf 31.2 MB English http://rapidshare.com/files/15686798/Gale_Encyclopedia_of_Alternative_Medicine__2nd_Edition._Vol._4__S-Z.pdf
Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine 2nd_Edition. Vol. 3 L-R Pdf 11.5 MB English http://rapidshare.com/files/15686797/Gale_Encyclopedia_of_Alternative_Medicine__2nd_Edition._Vol._3__L-R.pdf
Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine 2nd Edition Vol 2 D-K Pdf 33.5 MB English http://rapidshare.com/files/15686796/Gale_Encyclopedia_of_Alternative_Medicine__2nd_Edition._Vol._2__D-K.pdf
Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine 2nd Edition Vol 1 A-C Pdf 26.5 MB English http://rapidshare.com/files/15678032/Gale_Encyclopedia_of_Alternative_Medicine__2nd_Edition._Vol._1__A-C.pdf
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
8:39 AM
![]()
![]()
Natural Cure (ebook)
http://rapidshare.com/files/13369109/Kevin_Trudeau_s_Natural_Cures_Books__2nd_Edition_.rar
PW: dlvjak
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
8:31 AM
![]()
![]()
Protective effect of aqueous saffron extract
Cellular defense against free radical injury is provided by enzymatic (catalase, superoxide dismutases, and glutathione peroxidase) and nonenzymatic (GSH, α-tocopherol, vitamin C, and urate) free radical scavenging systems, present in the cell. Recent overwhelming attention to plant products and alternative medicine has encouraged plant chemists, pharmacologists, biochemists, and molecular biologists to combine their efforts in a search for natural agents that can limit free radicalmediated
injuries during and following ischemia– reperfusion, for better therapeutic management of IRI.
Crocus sativus L., commonly known as saffron, is used in folk medicine as an antispasmodic, eupeptic, gingival sedative, anticatarrhal, nerve sedative, carminative, diaphoteric, expectorant, stimulant, stomachic, aphrodisiac and emmenagogue. Furthermore, modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated that saffron extract or its active constituents have anticonvulsant, antidepressant, anti-inflammatory and antitumour effects, radical scavenger as well as learning and memory improving properties and promote the diffusivity of oxygen in different tissues. Saffron extract also has chemopreventive and showed protective effects on genotoxins-induced oxidative stress in Swiss albino mice.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:40 AM
![]()
![]()
Role of Black Seed Extracts and H2O2 in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells
Black seed (N. Sativa L) is an oriental spice of the family Ranunculaceae that has long been rationally used as a natural medicine for treatment of many acute as well as chronic conditions including cardiovascular disease and immunological disorders. It has been used in the treatment of diabetes, hypertension, and dermatological conditions. There have been very few studies on the effects of N. sativa as a chemoprevention of chronic diseases as well as in cancer prevention and/or therapy. Oxidative stress is a condition that underlies many acute as well as chronic conditions. The combination and role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in vivo is still a matter of conjecture. Our objective for the present study was to expose MCF-7 breast cancer cells in vitro (as a chronic disease example) to aqueous and alcohol extracts and in combination with H2O2 as an oxidative stressor. Measurement of cell survival under various concentrations and mixtures was conducted using standard cell culture techniques. The alcohol extract and its mixtures were able to influence the survival of MCF-7 cells. In contrast, H2O2 alone reduced effectively the survival of MCF-7 cells. N. Sativa alone or in combination with oxidative stress was found to be effective (in vitro) in influencing the survival of MCF-7 breast cancer cells, unveiling promising opportunities in the field of cancer chemoprevention and/or treatment.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:37 AM
![]()
![]()
Medicinal Value of Black cumin (Nigella sativa):
Black cumin seed has been used for centuries to treat respiratory and digestive problems, parasites, and inflammation. In ancient times, it was a remedy for a variety of health conditions including, colds, infections, headaches, and toothaches. Black cumin was also used as a remedy for skin diseases, dry skin, dandruff and wounds.
Many herbalists in current times embrace the healing properties of black cumin seed extract. For example, the extract is sometimes used externally to treat such skin care problems as psoriasis, eczema, and dry skin, and internally to treat stomach problems, respiratory ailments, and allergies, as well as to improve circulation and the immune system. In recent years, the extract has been the subject of immune system research.
One reason that is often given for the medicinal value of black cumin seed extract is its richness in polyunsaturated fatty acids, which help to produce prostaglandin E1. Prostaglandin E1 has many functions in the body, particularly in relation to the immune system, sugar metabolism, skin infections, and blood clots. It is also believed to protect the stomach lining.
Experts point out that the medicinal value may be provided by a unique and mysterious synergy (combined action) between the multitude of compounds present in the seeds. In addition, the extract, which is more concentrated than the seeds alone, is said to have greater healing power. A study at Cairo University in Eqypt showed a boost in antibacterial activity when the extract was used in combination with antibiotics such as streptomycin and gentamicin. In the same study, it showed additional antibacterial function in combination with erythromycin, tobramycin, doxycycline, and ampicillin, to kill E. coli and the pathogenic yeast, Candida albicans.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:36 AM
![]()
![]()
Kalonji (Nigella sativa), A Universal Remedy
Khalid Bin Saad states that he was travelling with Ghalib Bin Jabr, when fell ill during the journey. Ibn Abi Ateeq (nephew of Hazrat Aisha) Came to meet us. On seeing the patient, he took 5 or 7 seeds of Kalonji and ground it, mixed it in olive oil and dropped in both nostrils, Hazrat Aisha told us that Prophet Muhammad (Pbuh) stated that there was cure in black seeds for all ailments except sam. I asked him, what was sam? he told “Death”. Ghalib Bin Jabr became healthy with that treatment. Observations of the scholars of Hadith reveal that shooneez is equally effective for the diseases due to heat and cold. Zahbi states that kalonji removes the obstruction of any part of the body, expels the gases and strengthens the stomach. It is Emmenagogue, Lactogogue and Diuretic. It is an Anti-Helminthic, if taken with vinegar. It is useful in chronic cold. Inhalation of its smell is useful in common cold. The oil of Kalonji is effective in Alopecia. Half tea-spoonful, if boiled in water and taken, is helpful in Asthma and diffuses the toxic effects of Bee and Wasps. Continuous use of kalonji is effective in mad dog biting. Fumigation of kalonji is useful in respiratory diseases. It is useful in paralysis, Facial Palsy, Migraine, Amnesia and Palpitation. It is also an expectorant and antipyretic. It mormalises the secretions of stomach and pancreas. This phenomenon is very much effective and significant in the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. It expels the kidney and urinary bladder stones, if taken with the syrup of honey. It is effective in jaundice also if taken with milk. It’s powder if taken with water is effective in Haemorrhoids. If Kalonji seeds are boiled in vinegar and this solution is applied on Gums and Teeth, it removes the inflammation of the gums and relieves the pain also. It is also reported that its fine powder is effective if applied in early stages of cataract. Kalonji is also used in skin disorders. The oil of the seeds is also effective in earache. If it is taken with Qust Sheering after breakfast and Dinner, it is effective in chronic dysentery and Asthma. Qust Sheering is a good medicine for sexual debility, but if it is taken with Kalonji seeds and Habburrashad, it becomes more fortified. Modern upto date trials have proved that Kalonji seeds alone or in combination with other drugs are highly effective in Diabetes Mellitus, vitiligo and other skin ailments.
It is stated in the books of seerat that Nabi-e-Akram (Pbuh) himself used to take these seeds for therapeutic purpose but with the syrup of Honey.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:34 AM
![]()
![]()
Black Seed (Habba-tu Sawda), A Herbal Gift
The Black Seed has been used for over two thousand years. It has been said that the Black Seed should be used regularly because it has a cure for every disease except death. A special oil is extracted from the seed which is used in the preparation of various medical formulas. It has been used to treat bronchitis and coughs. Also it has been used to help increase body tone, as a digestive tonic, to quell belching, stimulates excretion of urine, dissolves wind, quells colic pain and stomach-gas colic, expels worms, benefits some skin allergies, stimulates menstrual period, and increases the flow of breast milk. If you add a few drops to coffee or tea it can help calm the nervous system, help pertussis, dry cough, asthma, and bronchial respiratory complaints. If you take the Black Seed oil unmixed or undiluted it can produce gripe, and irritate the digestive system. The Black Seed acts as an expectorant by stimulating the body's energy and helping it to recover from fatigue and dispiritedness. (Medicine of the Prophet)
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:33 AM
![]()
![]()
Radical Scavenging Activity of Black Cumin, Coriander and Niger
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:31 AM
![]()
![]()
Black Seed and Ayurveda a medicine
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:30 AM
![]()
![]()
Black Seed and its benefited
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:29 AM
![]()
![]()
Role of Neem in pregnancy
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:27 AM
![]()
![]()
Nigella sativa, Anti-bacterial and Anti-tumor Property
Using an active principle of fatty acids derived from black seed, studies with Swiss albino mice showed that this active principle could completely inhibit the development of a common type of cancer cells called Ehrlich ascites carcinoma (EAC). A second common type of cancer cells, Dalton's lymphoma ascites (DLA) cells were also used.
The Mice which had received the EAC cells and black seed remained normal without any tumor formation, illustrating that the active principle was 100% effective in preventing EAC tumor development.
The mice who received DLA cells and black seed showed that the active principle had inhibited tumor development by 50% less compared to mice not given the active principle.
It is evident that the active principle isolated from Nigella sativa seeds is a potent anti-tumor agent, and the constituent long chain fatty acid may be the main active component.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
3:24 AM
![]()
![]()
Wednesday, August 1, 2007
Neem Extract, A Inhibitory Effect
Inhibitory effect of aqueous Neem extract upon plaque formation:
Inhibitory effects of aqueous extracts derived from the bark-containing sticks (Neem stick) of Azadirachta indica upon bacterial aggregation, growth, adhesion to hydroxyapatite, and production of insoluble glucan, which may affect in vitro plaque formation. Neem stick extracts were screened for minimal bacterial growth inhibition (MIC) against a panel of streptococci by means of a broth dilution assay. Initial bacterial attachment was quantified by the measurement of the adhesion of 3H-labeled Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-conditioned synthetic hydroxyapatite. The effect of the Neem stick extract upon insoluble glucan synthesis was measured by the uptake of radiolabeled glucose from 14C-sucrose. Aggregating activity of the Neem stick extracts upon a panel of streptococci was also examined. No inhibition of bacterial growth was observed among the streptococcal strains tested in the presence of < or = 320 mg/mL of the Neem stick extract. The pre-treatment of S. sanguis with the Neem stick extract or the gallotannin-enriched extract from Melaphis chinensis at 250 mg/mL resulted in a significant inhibition of the bacterial adhesion to saliva-conditioned hydroxyapatite. Pre-treatment of salivaconditioned hydroxyapatite with the Neem stick or gallotannin-rich extract prior to exposure to bacteria yielded significant reductions in bacterial adhesion. The Neem stick extract and the gallotannin-enriched extract from Melaphis chinensis inhibited insoluble glucan synthesis. Incubation of oral streptococci with the Neem stick extract resulted in a microscopically observable bacteria aggregation.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:31 AM
![]()
![]()
Neem Leaf, A Herbal Medicine
Neem Leaf, A Multi Treatment Herbs:
Azadirachta indica, commonly known as neem, has attracted worldwide prominence in recent years, owing to its wide range of medicinal properties. Neem has been extensively used in Ayurveda, Unani and Homoeopathic medicine and has become a cynosure of modern medicine. Neem elaborates a vast array of biologically active compounds that are chemically diverse and structurally complex. More than 140 compounds have been isolated from different parts of neem. All parts of the neem tree leaves, flowers, seeds, fruits, roots and bark have been used traditionally for the treatment of inflammation, infections, fever, skin diseases and dental disorders. The medicinal utilities have been described especially for neem leaf. Neem leaf and its constituents have been demonstrated to exhibit immunomodulatory, antiinflammatory, antihyperglycaemic, antiulcer, antimalarial, antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral, antioxidant, antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic properties.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
1:13 AM
![]()
![]()
Cytokine Signaling Pathway
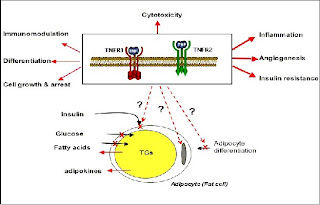
Historically, cytokines have attracted much interest due to their ability to induce cellular demise. This toxicity often requires high circulating levels, as is observed during ischemia-reperfusion damage, graft-versus-host disease, cerebral malaria, sepsis, cachexia and cancer. However, chronic exposure to low levels of cytokines can also exert profound effects. These latter actions have been shown to alter multiple cellular functions and may play a physiological role in regulating cellular metabolism, tissue development, thermo genesis and appetite. The research interests focus on the actions of the prototypical cytokine, TNF alpha and the signalling mechanisms by which its actions are manifested in adipose tissue.
TNF alpha (Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha) is a multifunctional cytokine that mediates its effects via two cell surface receptors. These are ubiquitously expressed and differ primarily in their intracellular signalling domains. Both TNF and its receptors are produced by adipose tissue where it can affect normal adipocyte development as well as key functions such as insulin sensitivity, triglyceride storage and release and adipokine production. These actions can themselves go on to impact on systemic sites and alter whole body energy homeostasis. Understanding how TNF signals in adipocytes is important if we wish to identify novel targets for therapeutic intervention in obesity-related metabolic disorders. To this end, scientists currently investigating the mechanisms of TNF signalling in insulin resistance, adipocyte development and gene expression.
Posted by
jawed iqbal
at
12:32 AM
![]()
![]()